low flow low gradient aortic stenosis review
Severe aortic stenosis is defined by a mean gradient 30 mm Hg at any time during the dobutamine study provided the effective orifice area stays 12 cm 2. On multivariable analysis chronic obstructive pulmonary disease p 002 and lower hemoglobin values p 0001 were associated with increased all-cause mortality.
Low-flow low-gradient LF-LG aortic stenosis AS may occur with depressed or preserved left ventricular ejection fraction LVEF and both situations are among the most challenging encountered in patients with valvular heart disease.

. A small aortic valve area AVA. With this hemodynamic presentation it is difficult to distinguish true aortic valve stenosis where the primary culprit is. AVA.
Of patients with severe AS 30 to 50 present with low-flowlow-gradient AS LFLGAS status. Purpose of review. The presence of LV contractile reserve during DSE was observed in 45 of patients.
LF LG AS is characterized by combination of severe aortic valve stenosis calculated aortic valve area AVA low transvalvular gradient mean gradient low flow stroke volume 35 mlm 2. Low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis however is an especially challenging subset as valve replacement has a significant risk and may fail to alleviate symptoms or improve left ventricular function. The purpose of this review is to highlight the diagnostic and management specificities of this entity.
The severity of low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis cases continue to be misunderstood because of challenging diagnosis and treatment remains complexWe discuss current diagnostic and treatment modalities for low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis. In both cases the decrease in gradient relative to AS severity is due to a reduction in transvalvular flow. Various diagnostic modalities are needed to accurately determine the severity of aortic stenosis and potential treatment benefit.
With regard to prognosis and to management decisions it is essential to distinguish those patients with preserved systolic left ventricular ejection fraction from patients with impaired systolic left ventricular ejection fraction and in particular those with. Low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis LFLG AS is an echocardiographic entity defined by a mismatch between a reduced aortic valve area AVA 1 cm 2 and a non-severe increase of transvalvular mean pressure gradient MPG 40 mmHg with an impaired stroke volume at rest SV index 35 mlm 2 1 2. LF LG AS is characterized by combination of severe aortic valve stenosis calculated aortic valve area AVA low transvalvular gradient mean gradient low flow stroke volume 35 mlm 2.
Conclusion In patients with low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis the most significant risk factors for poor outcome were 1 impaired functional capacity as measured by Duke Activity Status Index or 6-minute walk test distance. LFLG AS still puts the clinicians in front of. An important proportion of patients with aortic stenosis AS have a low-gradient AS ie.
Aortic stenosis AS is a complex systemic valvular and vascular disease with a high prevalence in developed countries. 40 ms a mean gradient 40 mm Hg or an aortic valve area. This article summarizes current guidelines and best practices for the management of.
Low gradient low flow aortic stenosis is defined by a left ventricular ejection fraction 40 mean gradient 30 mm Hg and effective orifice area 10 cm 2. Left ventricular LV systolic dysfunction defined as LV ejec-. This review explores low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis from a heart failure perspective describing the mechanisms and consequences for diagnosis prognosis and management.
True-severe classical and paradoxical low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis can be distinguished from pseudo-severe aortic stenosis by dobutamine stress. Low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis is a difficult entity to diagnose and treat. 2 more severe valve stenosis as measured by projected aortic valve area at a normal transvalvular flow rate.
Projected valve area at normal flow rate improves the assessment of stenosis severity in patients with low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis. The management of this subset of patients is particularly challenging because the AVA-gradient discrepancy raises. Left in paradoxical low-gradient AS right the primary resistor is at the level of the vasculature and not the valve.
Aortic stenosis AS is defined as a peak aortic jet velocity. This article reviews the potential problems in evaluating aortic stenosis severity in low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis the utility of dobutamine challenge to identify patients most. However as many as 30 of patients who have a calculated AVA in the severe range have other parameters suggesting mild or moderate disease ie mean gradient low-flowlow-gradient AS LFLGAS may truly have severe AS with resultant myocardial failure true AS or may have more moderate degrees of AS and unrelated.
An important proportion of patients with aortic stenosis AS have a low-gradient AS ie. The management of this subset of patients is particularly challenging because the AVA-gradient discrepancy raises uncertainty about the. The Multicenter TOPAS Truly or Pseudo-Severe Aortic Stenosis Study.
In contrast to severe aortic stenosis AS. A small aortic valve area AVA. Aortic valve replacement AVR if the patient has symptoms or.
Dobutamine stress echocardiography is necessary. Mortality rates were 38 201 and 323 at 30 days 1 year and 2 years respectively. Low flow low gradient aortic stenosis is a highly challenging condition in terms of diagnosis and therapeutic management.
During the symptomatic stage the rate of death increases dramatically so that a precise diagnostic approach is taken to guide therapeutic options. It implies aortic stenosis of. The review clarifies that low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis does not necessarily imply severe aortic stenosis with consequent low-flow.
The occurrence of low-flow low-gradient severe aortic stenosis in patients with normal left ventricle LV ejection fraction has only been recently described. Valvular stress testing with nitroprusside or symptom-limited exercise examining the pulmonary artery wedge pressure PAWP mean gradient MG and stroke volume SV can unmask the underlying. Aortic stenosis AS is the most frequently observed valvular heart disease.
With this hemodynamic presentation it is difficult to distinguish true aortic valve stenosis where the primary culprit is severe aortic valve disease. The new entity paradoxical low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis refers to cases in which patients have severe AS based on assessment of aortic valve area AVA 1 cm2 or indexed AVA 06 cm2m2 but paradoxically have a low mean.
Role Of Advanced Left Ventricular Imaging In Adults With Aortic Stenosis Heart

Transvalvular Flow Rate Determines Prognostic Value Of Aortic Valve Area In Aortic Stenosis Abstract Europe Pmc

Excess Mortality Associated With Progression Rate In Asymptomatic Aortic Valve Stenosis Journal Of The American Society Of Echocardiography

Aortic Stenosis Low Flow Low Gradient What S The Hype Aortic Stenosis Stenosis Gradient

Differential Diagnosis Of Low Gradient Severe Aortic Stenosis Download Scientific Diagram

Representative Pressure Volume Curves Of Normal Flow High Gradient Download Scientific Diagram

Figure 1 From Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis Semantic Scholar

Aortic Stenosis Low Flow Low Gradient What S The Hype Aortic Stenosis Stenosis Tricuspid Valve

Pdf Assessment Of Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis Multimodality Imaging Is The Key To Success Semantic Scholar

Pdf Assessment Of Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis Multimodality Imaging Is The Key To Success Semantic Scholar

Pdf Assessment Of Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis Multimodality Imaging Is The Key To Success Semantic Scholar

Figure 1 From Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis Semantic Scholar

Pdf Assessment Of Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis Multimodality Imaging Is The Key To Success Semantic Scholar

Impact Of The Use Of The Multiview Approach And Correction For Pressure Download Scientific Diagram

Figure 1 From Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis Semantic Scholar

Figure 1 From Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis Semantic Scholar

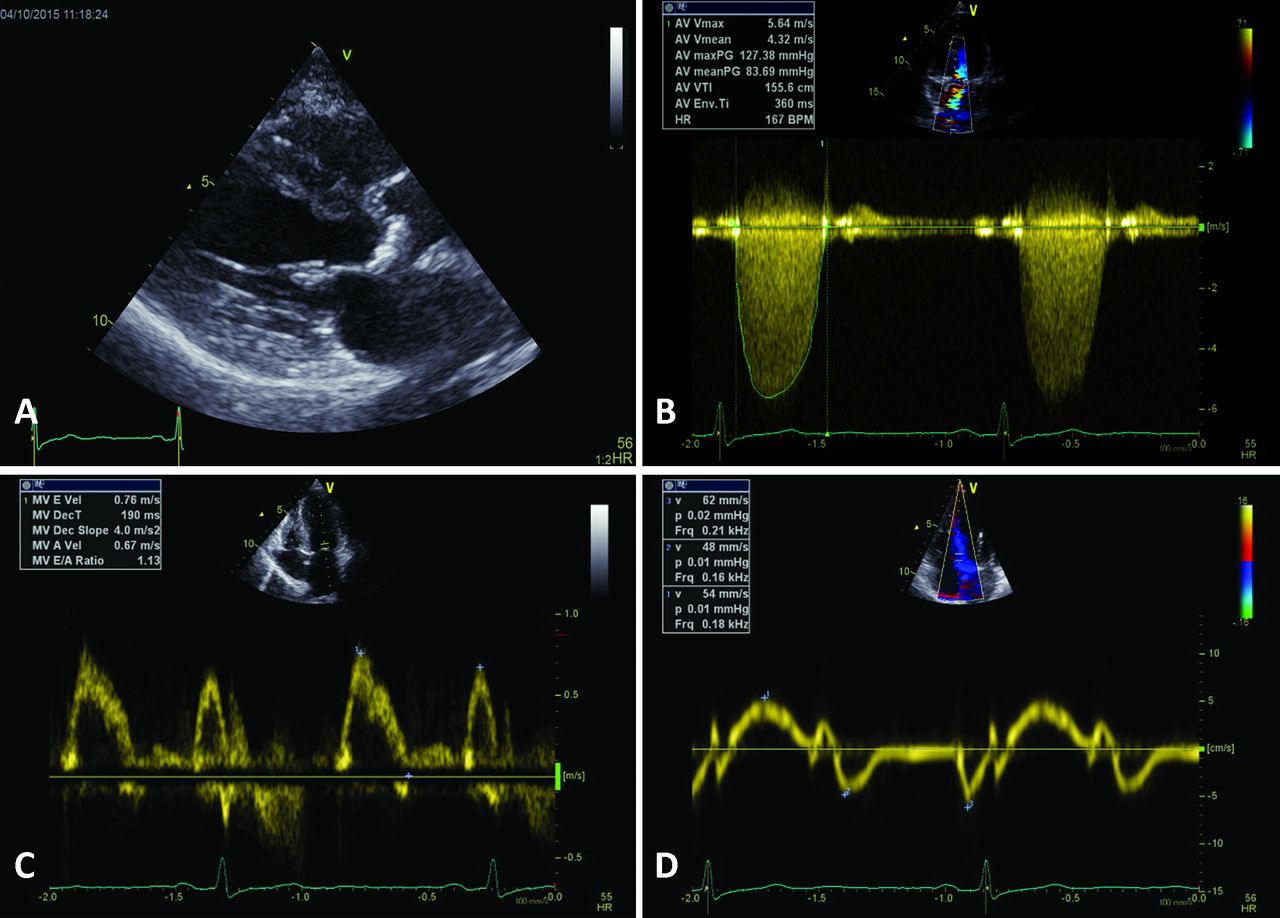
Case Of Classical Low Flow Low Gradient As With Pseudo Severe Stenosis Download Scientific Diagram

Pdf Assessment Of Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis Multimodality Imaging Is The Key To Success Semantic Scholar

Case Of Classical Low Flow Low Gradient As With Pseudo Severe Stenosis Download Scientific Diagram
